Burns and Management
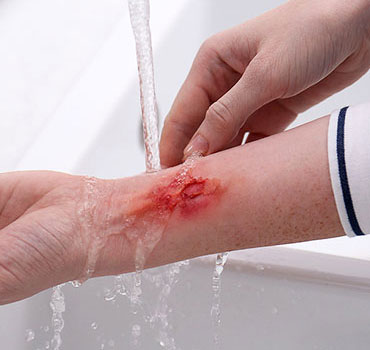
Burn injuries occur when heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation damage the skin, leading to various degrees of tissue destruction. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeons specialize in burn treatment, wound healing, and aesthetic restoration to improve function and appearance while preventing complications.
What Are Burns?
- A burn occurs when heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation come into contact with the skin, causing tissue damage.
- Most burns happen accidentally in homes, workplaces, or industrial settings.
- Burns are classified based on severity, which helps plastic surgeons determine the treatment approach.
- Timely treatment is critical—if left untreated, burns can lead to infection, scarring, or deformities.
How Common Are Burns?
Burns are fairly common, especially among:- Children (accidental burns at home)
- Workplace injuries (industrial burns)
- Kitchen accidents (hot oil, steam)
- Chemical exposure injuries
Who Treats Burns?
Board-certified plastic surgeons specialize in burn treatment and reconstruction to restore both function and aesthetics.
Degrees of Burns
1. First-Degree Burns:- Mild burns affecting the epidermis (outer skin layer)
- Causes redness, pain, and swelling but no blisters
- Example: Sunburn
- Extends into the dermal layer (deeper skin layer)
- Causes severe pain, redness, swelling, and blisters
- Destroys all skin layers including hair follicles and sweat glands
- Affected skin appears white, leathery, or charred
- Since nerve endings are damaged, there may be less pain in the burned area
- The most severe burns, extending into muscles, tendons, and bones
- Requires urgent hospitalization and can be life-threatening
What Causes Burns?
- Thermal Burns – Fire, hot liquids (boiling water, oil), steam, hot surfaces
- Chemical Burns – Acid, cement, drain cleaners, caustic substances
- Electrical Burns – High-voltage or low-voltage electric shocks
- Radiation Burns – Exposure to UV light, radiation therapy
Signs & Symptoms of Burns
Symptoms depend on the degree and severity of the burn and the causative factor. Common symptoms include:
- Blisters
- Pain and swelling
- White, leathery, or charred skin
- Peeling skin
- Dehydration
How Are Burns Diagnosed?
- Minor Burns: 1st & 2nd-degree burns covering less than 10% of body surface area
- Moderate Burns: 2nd-degree burns covering about 10% of body surface area (face, hands, feet, genitals are considered severe)
- Severe Burns:
3rd-degree burns covering more than 1% of body surface area
Facial burns (high risk due to airway involvement)
Flame burns (risk of respiratory damage)
Children with burns over 10% may require hospitalization for better pain control and management
Surgical Management of Burns
- Wound Debridement – Removal of dead tissue for faster healing
- Skin Grafting – Transplanting healthy skin to cover burn wounds
- Flap Surgery – Uses healthy tissue for large burn reconstruction
- Contracture Release Surgery – Improves mobility if scars restrict movement
- Scar Revision & Laser Therapy – Minimizes burn scars
Benefits of Burn Surgery & Management
- Faster Healing – Reduces risk of infection and complications
- Restores Skin Function – Improves movement in affected areas
- Reduces Scarring & Deformities – Enhances aesthetic appearance
- Prevents Contractures – Maintains flexibility of skin and joints
- Boosts Self-Confidence – Helps patients regain normal life
